India’s space agency, ISRO, has launched a new observatory in space, called Xposat. This observatory will study cosmic sources of X-rays, such as black holes, neutron stars, and pulsars. Xposat is expected to enhance India’s capabilities in space science and exploration, as well as contribute to global knowledge of the universe.
What is Xposat and Why is it Important?
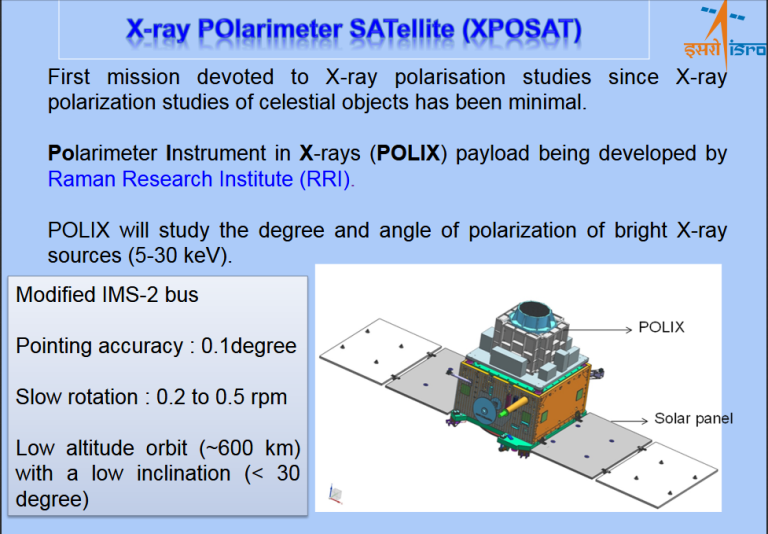
Xposat stands for X-ray Polarimeter Satellite. It is a small satellite, weighing about 250 kg, that carries a payload of two instruments: a polarimeter and a spectrometer. The polarimeter will measure the polarization of X-rays, which is a property that reveals the orientation and shape of the emitting source. The spectrometer will measure the energy and intensity of X-rays, which can provide information about the temperature, density, and composition of the source.
Xposat will observe about 40 cosmic sources of X-rays, including some of the most exotic and mysterious objects in the universe. These include black holes, which are regions of space where gravity is so strong that nothing can escape, not even light; neutron stars, which are the remnants of massive stars that have collapsed under their own gravity; and pulsars, which are rapidly rotating neutron stars that emit beams of radiation.
Xposat will help scientists understand how these objects form, evolve, and interact with their surroundings. It will also test some of the fundamental theories of physics, such as general relativity and quantum mechanics, in extreme conditions. Xposat will also explore the origin and evolution of cosmic magnetic fields, which play a crucial role in shaping the structure and dynamics of the universe.
How Will Xposat Benefit India and the World?
Xposat is a milestone for India’s space program, as it is the first dedicated mission for X-ray astronomy. India has previously participated in some international collaborations for X-ray observations, such as the AstroSat mission, which was launched in 2015. However, Xposat will give India more autonomy and flexibility in choosing and studying its own targets of interest.
Xposat will also boost India’s scientific and technological capabilities, as it involves the development and operation of sophisticated instruments and software. Xposat will generate a large amount of data, which will require advanced analysis and interpretation. Xposat will also provide opportunities for training and education of young scientists and engineers, as well as inspire the next generation of space enthusiasts.
Xposat will also contribute to the global scientific community, as it will share its data and findings with other researchers and institutions. Xposat will complement and collaborate with other existing and planned X-ray observatories, such as NASA’s Chandra and ESA’s XMM-Newton. Xposat will also pave the way for future missions, such as LISA, which will detect gravitational waves from merging black holes and neutron stars.
Xposat is a shining example of how India is pursuing its ambitions and aspirations in space science and exploration. Xposat will not only illuminate the dark and mysterious corners of the universe, but also brighten the prospects and potential of India’s space program.



